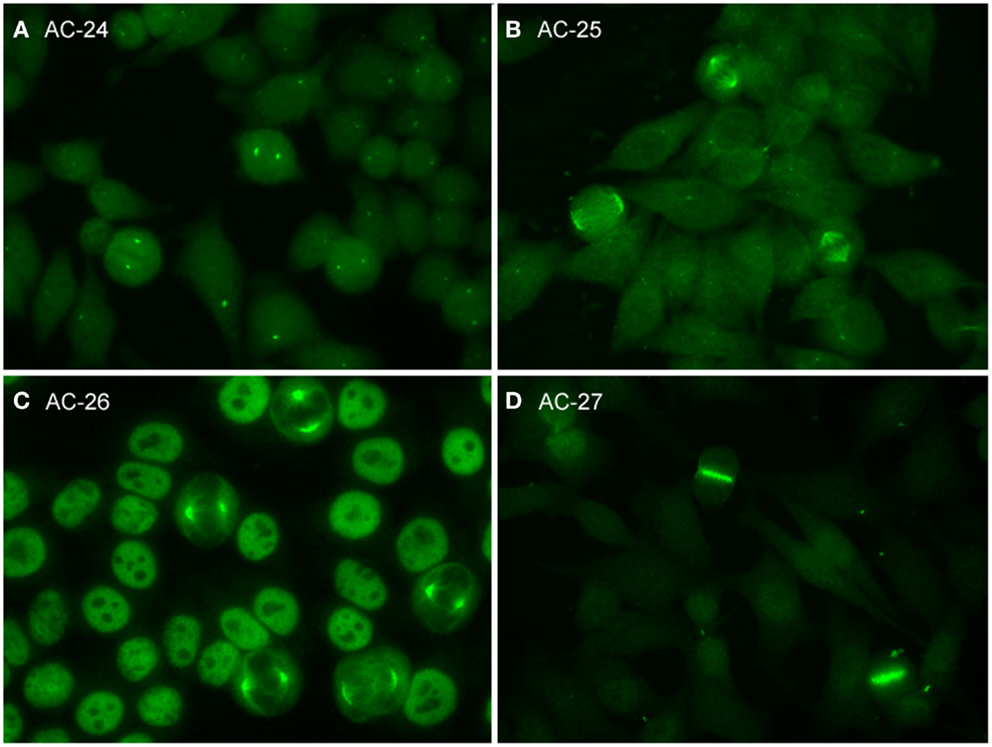
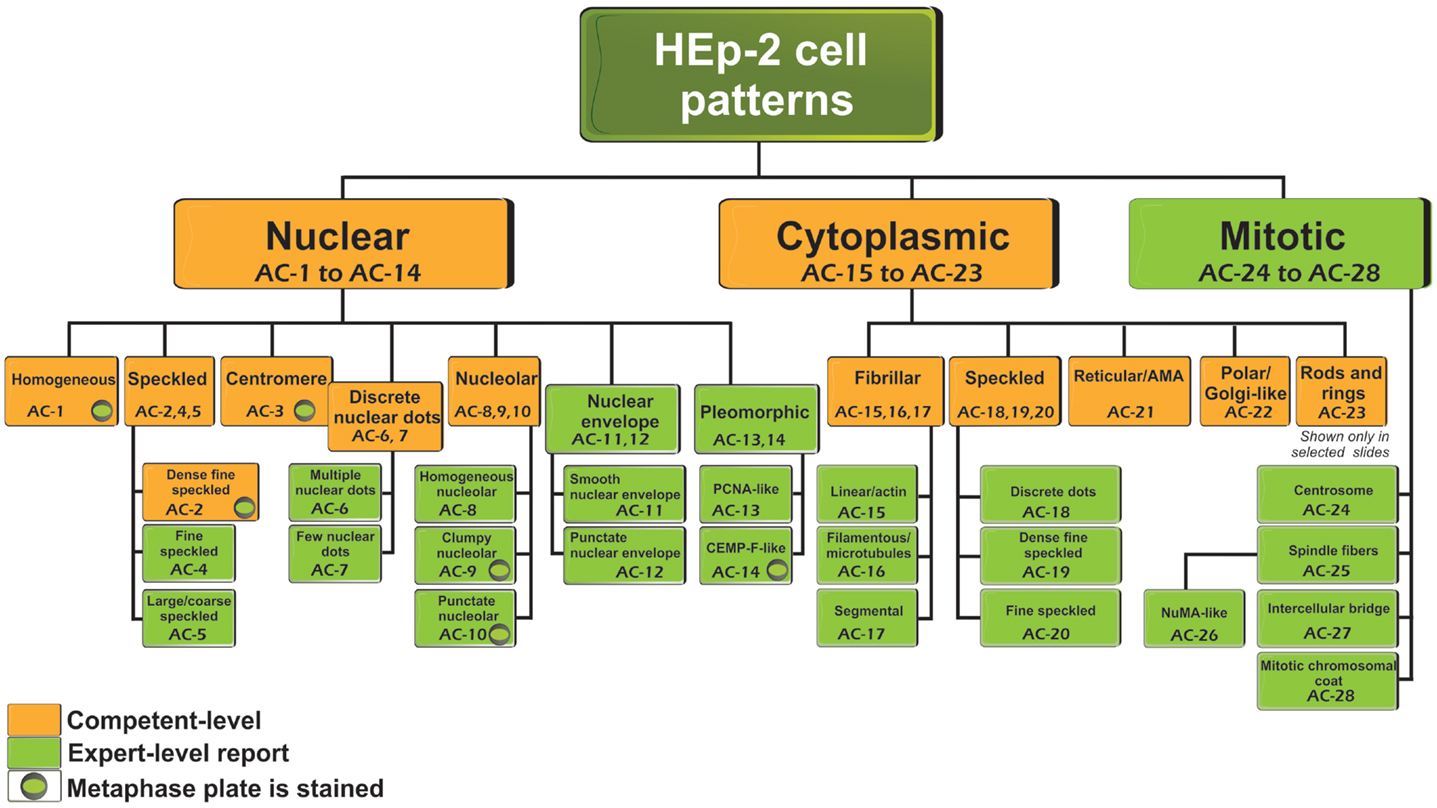
Hep2 Cell Patterns
Hep2 Cell Patterns - This clinical relevance is primarily defined within the context of the suspected disease and includes recommendations for. Web it allows detection of antibody binding to specific intracellular targets, resulting in diverse staining patterns that are usually categorized based on the cellular components recognized and the degree of binding, as reflected by the fluorescence intensity or titer [ 2, 3 ]. The nuclear dense fine speckled pattern occurred only in healthy individuals. International consensus on ana patterns. Many patients with sle have more than one type of pattern. The consensus paper has been published in annals of the rheumatic diseases.1. Homogenous, speckled, centromere, nucleolar, and nuclear dots. Experienced cl defined as reporting all 3 main nomenclature categories. Web assess antinuclear antibody titers and patterns were retrospectively identified and compared by iifa using human epithelial cells (hep‐2) and primate liver tissue substrate according to international consensus in sard. These patterns are the result of autoantibody binding. Web it allows detection of antibody binding to specific intracellular targets, resulting in diverse staining patterns that are usually categorized based on the cellular components recognized and the degree of binding, as reflected by the fluorescence intensity or titer [ 2, 3 ]. The nuclear dense fine speckled pattern occurred only in healthy individuals. Homogenous, speckled, centromere, nucleolar, and nuclear dots. The dichotomous outcome, negative or positive, is integrated in diagnostic and classification criteria for. Experienced cl defined as reporting all 3 main nomenclature categories. The consensus paper has been published in annals of the rheumatic diseases.1. Web the ana pattern profile was distinct in the 2 groups. Serum complement 3 (c3), c4, and immunoglobulin g were compared among subgroups with different ana titers. Nuclear homogeneous, nuclear coarse speckled, and nuclear centromeric patterns appeared exclusively in patients with ards. It still leaves open the question of. Web assess antinuclear antibody titers and patterns were retrospectively identified and compared by iifa using human epithelial cells (hep‐2) and primate liver tissue substrate according to international consensus in sard. Experienced cl defined as reporting all 3 main nomenclature categories. Web the ana pattern profile was distinct in the 2 groups. Serum complement 3 (c3), c4, and immunoglobulin g were. Serum complement 3 (c3), c4, and immunoglobulin g were compared among subgroups with different ana titers. The nuclear dense fine speckled pattern occurred only in healthy individuals. These patterns are the result of autoantibody binding. Many patients with sle have more than one type of pattern. This clinical relevance is primarily defined within the context of the suspected disease and. This is a summary of the international consensus on antinuclear antibody pattern (icap) meeting and subsequent discussion, debate, and dialog. These patterns are the result of autoantibody binding. Experienced cl defined as reporting all 3 main nomenclature categories. Interphase cells show homogeneous nuclear staining while mitotic cells show staining of the condensed chromosome regions. The dichotomous outcome, negative or positive,. The consensus paper has been published in annals of the rheumatic diseases.1. International consensus on ana patterns. These patterns are the result of autoantibody binding. The nuclear dense fine speckled pattern occurred only in healthy individuals. Interphase cells show homogeneous nuclear staining while mitotic cells show staining of the condensed chromosome regions. Web assess antinuclear antibody titers and patterns were retrospectively identified and compared by iifa using human epithelial cells (hep‐2) and primate liver tissue substrate according to international consensus in sard. Many patients with sle have more than one type of pattern. Web the ana pattern profile was distinct in the 2 groups. The dichotomous outcome, negative or positive, is integrated. Homogenous, speckled, centromere, nucleolar, and nuclear dots. This clinical relevance is primarily defined within the context of the suspected disease and includes recommendations for. The consensus paper has been published in annals of the rheumatic diseases.1. International consensus on ana patterns. Interphase cells show homogeneous nuclear staining while mitotic cells show staining of the condensed chromosome regions. It still leaves open the question of. Web it allows detection of antibody binding to specific intracellular targets, resulting in diverse staining patterns that are usually categorized based on the cellular components recognized and the degree of binding, as reflected by the fluorescence intensity or titer [ 2, 3 ]. This clinical relevance is primarily defined within the context of. International consensus on ana patterns. Serum complement 3 (c3), c4, and immunoglobulin g were compared among subgroups with different ana titers. Homogenous, speckled, centromere, nucleolar, and nuclear dots. The dichotomous outcome, negative or positive, is integrated in diagnostic and classification criteria for. The nuclear dense fine speckled pattern occurred only in healthy individuals. Many patients with sle have more than one type of pattern. Experienced cl defined as reporting all 3 main nomenclature categories. We conclude hereby that synucleinopathies are not associated with detectable presence of ana in plasma. Nuclear homogeneous, nuclear coarse speckled, and nuclear centromeric patterns appeared exclusively in patients with ards. Interphase cells show homogeneous nuclear staining while mitotic cells. Interphase cells show homogeneous nuclear staining while mitotic cells show staining of the condensed chromosome regions. Serum complement 3 (c3), c4, and immunoglobulin g were compared among subgroups with different ana titers. Web assess antinuclear antibody titers and patterns were retrospectively identified and compared by iifa using human epithelial cells (hep‐2) and primate liver tissue substrate according to international consensus. This is a summary of the international consensus on antinuclear antibody pattern (icap) meeting and subsequent discussion, debate, and dialog. The consensus paper has been published in annals of the rheumatic diseases.1. We conclude hereby that synucleinopathies are not associated with detectable presence of ana in plasma. It still leaves open the question of. Homogenous, speckled, centromere, nucleolar, and nuclear dots. Web the ana pattern profile was distinct in the 2 groups. Experienced cl defined as reporting all 3 main nomenclature categories. Many patients with sle have more than one type of pattern. International consensus on ana patterns. These patterns are the result of autoantibody binding. Web it allows detection of antibody binding to specific intracellular targets, resulting in diverse staining patterns that are usually categorized based on the cellular components recognized and the degree of binding, as reflected by the fluorescence intensity or titer [ 2, 3 ]. Serum complement 3 (c3), c4, and immunoglobulin g were compared among subgroups with different ana titers. This clinical relevance is primarily defined within the context of the suspected disease and includes recommendations for. The nuclear dense fine speckled pattern occurred only in healthy individuals. Representative images of selected major HEp2 cell patterns. (A
Representative images of selected major HEp2 cell patterns. (A
Figure 1 from The Classification of HEp2 Cell Patterns Using Fractal
2. IFA Pattern recognition & HEp2 cell components YouTube
Frontiers Report of the First International Consensus on Standardized
Display of HEp2 cell pattern classification agreement and disagreement
The surface of six Hep2 cell patterns. Download Scientific Diagram
HEp2 staining patterns 1) Homogeneous 2) Nucleolar 3) Coarse Speckled
Figure 1 from The Clinical Significance of the Dense Fine Speckled
Frontiers Report of the First International Consensus on Standardized
Nuclear Homogeneous, Nuclear Coarse Speckled, And Nuclear Centromeric Patterns Appeared Exclusively In Patients With Ards.
Web Assess Antinuclear Antibody Titers And Patterns Were Retrospectively Identified And Compared By Iifa Using Human Epithelial Cells (Hep‐2) And Primate Liver Tissue Substrate According To International Consensus In Sard.
The Dichotomous Outcome, Negative Or Positive, Is Integrated In Diagnostic And Classification Criteria For.
Interphase Cells Show Homogeneous Nuclear Staining While Mitotic Cells Show Staining Of The Condensed Chromosome Regions.
Related Post: